VitalAid Inc. manufactures a vacuum-sealed high-protein food supplement that it sells to food aid organizations around the world. The company uses variable costing in conjunction with a standard costing system and has established the following standards for one package of VitalAid bars:
| Standard Quantity or Hours | Standard Price or Rate | Standard Cost | |||||
| Direct materials | 350 | grams | $ | 12.00 | per kg | $ | 4.20 |
| Direct labour | 0.25 | hours | $ | 13.00 | per hour | 3.25 | |
| Variable manufacturing overhead | 0.5 | hours | $ | 1.60 | per hour | 0.80 | |
| Total standard variable cost | $ | 8.25 | |||||
During October, the company recorded the following activity relative to production of VitalAid:
- The company produced 4,000 packages during October.
- A total of 1,800 kilograms of material was purchased at a cost of $19,800.
- There was no beginning inventory of materials; however, at the end of the month, 300 kilograms of material remained in ending inventory.
- The company employs 5 people to work on the production of VitalAid. During October, each employee worked an average of 185 hours at an average rate of $14.00 per hour.
- Variable manufacturing overhead is assigned to VitalAid on the basis of direct labour-hours. Variable manufacturing overhead costs during October totalled $1,850.
The company’s management is anxious to determine the efficiency of the VitalAid production activities.
Required:
1. For direct materials used in the production of VitalAid:
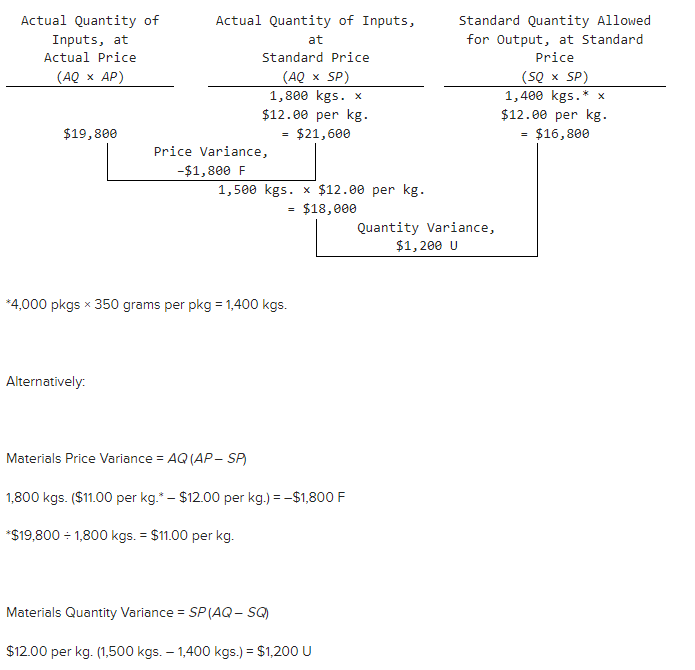
a. Compute the price and quantity variances. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting “F” for favorable, “U” for unfavorable, and “None” for no effect (i.e., zero variance).)
This part of the question is not part of your Connect assignment.
2. For labour employed in the production of VitalAid:
a. Compute the rate and efficiency variances. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting “F” for favorable, “U” for unfavorable, and “None” for no effect (i.e., zero variance).)
b. This part of the question is not part of your Connect assignment.
3-a. Compute the variable overhead spending and efficiency variances. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting “F” for favorable, “U” for unfavorable, and “None” for no effect (i.e., zero variance).)
Solution
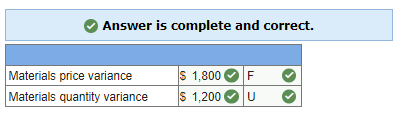
In the solution below, the materials price variance is computed on the entire amount of materials purchased, whereas the materials quantity variance is computed only on the amount of materials used in production:
Please click on the Icon below to purchase the full 100% CORRECT ANSWER at only $3




