Module 12 Assignment
Question 1
Question text – Estimating Cost of Capital Measures
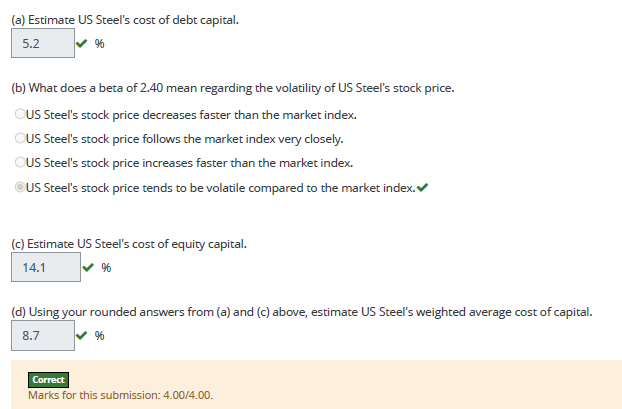
US Steel has $2.66 billion in total debt (which approximates its market value). Interest expense for the year was about $176.0 million. The company’s market capitalization is approximately $1.74 billion, its market beta is 2.40, and its assumed tax rate is 21%. Assume that the risk-free rate equals 2.1% and the market premium equals 5%.
Rounding Instructions: Do not round until your final answers. Round answers to one decimal place.
(a) Estimate US Steel’s cost of debt capital.
(b) What does a beta of 2.40 mean regarding the volatility of US Steel’s stock price. US Steel’s stock price decreases faster than the market index.US Steel’s stock price follows the market index very closely.US Steel’s stock price increases faster than the market index.US Steel’s stock price tends to be volatile compared to the market index.
(c) Estimate US Steel’s cost of equity capital.
(d) Using your rounded answers from (a) and (c) above, estimate US Steel’s weighted average cost of capital.
Solution
…Please click on the Icon below to purchase the FULL SOLUTION PACKAGE at only $10
See also: (Solved) Module 13 Assignment Estimating Share Value Using the DCF Model
Question 2 – Cost of Capital Measures
Question text – Estimating Market and Book Values and Cost of Capital Measures
The December 31, 2018, partial balance sheet of 3M Company follows (amounts in millions, except share and per share amounts). YCharts.com reported that the total market capitalization of 3M was $108.46 billion and its stock price was $190.54 as of December 31, 2018. Also, YCharts.com estimates its total enterprise value at $119.84 billion, and its market beta at 1.14. 3M’s average pretax borrowing cost is 2.07%, and its assumed statutory tax rate is 21%. Assume that the risk-free rate equals 2.1% and the market premium equals 5%.
| Liabilities | |
| Current liabilities | |
| Short-term borrowings and current portion of long-term debt | $1,211 |
| Accounts payable | 2,266 |
| Accrued payroll | 749 |
| Accrued income taxes | 243 |
| Other current liabilities | 2,775 |
| Total current liabilities | 7,244 |
| Long-term debt | 13,411 |
| Pension and post-retirement benefits | 2,987 |
| Other liabilities | 3,010 |
| Total liabilities | 26,652 |
| Equity | |
| 3M Company shareholders’ equity: | |
| Common stock,par value $0.01 per share Shares outstanding-2018: 576,575,168 | $ 9 |
| Additional paid-in capital | 5,643 |
| Retained earnings | 40,636 |
| Treasury stock | (29,626) |
| Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) | (6,866) |
| Total 3M Company shareholders’ equity | 9,796 |
| Noncontrolling interest | 52 |
| Total equity | 9,848 |
| Total liabilities and equity | $36,500 |
(a) Verify Ycharts.com’s computation of 3M’s market capitalization using the data from its financial report excerpts above. (Round your answer to two decimal places.)
(b) Compute the book value of 3M’s long-term debt as of December 31, 2018.
(c) Compute the market value of 3M’s debt using the data from Ycharts.com. (Round your answer to two decimal places.)
(d) Identify reasons behind the difference between the amounts computed in parts (b) and (c). (Select all that apply.)
The market price of 3M’s debt changed in value on December 31, 2018.
The market value of debt doesn’t include the issuing of new treasury stock.
The market value and book value of debt differs due to accounting usage of historical cost.
Ycharts.com might include other liabilities, such as lease obligations, in the calculation of debt.
(e) Compute 3M’s cost of debt capital. (Round your answer to one decimal place.)
(f) Compute 3M’s cost of equity capital. (Round your answer to one decimal place.)
(g) Using your rounded answer from (e) and (f) above, compute 3M’s weighted average cost of capital. Use the market capitalization from Ycharts.com and your rounded answer from (c) above for this calculation.
Do not round until your final answer. Round answer to one decimal place.
Feedback
Correct
Marks for this submission: 12.00/12.00.
…Please click on the Icon below to purchase the FULL SOLUTION PACKAGE at only $10
See also: (Solved) Module 14 Assignment – Estimating Share Value Using the ROPI Model
Question 3 – Cost of Capital Measures
Question text
Estimating Components of both WACC and DDM
An analyst estimates the cost of debt capital for Abbott Laboratories is 3.0% and that its cost of equity capital is 5.0%. Assume that ABT’s statutory tax rate is 21%, the risk-free rate is 2.1%, the market risk premium is 5%, the ABT market price is $84.10 per common share, and its dividends are $1.28 per common share.
(a) Compute ABT’s average pretax borrowing rate and its market beta. (Round your answers to one decimal place.)
(b) Assume that its dividends continue at the current level in perpetuity. Use the constant perpetuity dividend discount model to infer the market’s expected cost of equity capital. (Hint: Use Price per share = Dividends per share/Cost of equity capital.) (Round your answer to one decimal place.)
(c) Compare the inferred cost of equity capital from part (b) to the 5.0% estimated cost of equity capital from analysts.
- The inferred cost of equity capital seems high compared to 5.0%, which suggests that the investment has a negative beta.
- The inferred cost of equity capital seems low compared to 5.0%, which suggests that the investment has a negative beta.
- The inferred cost of equity capital seems high compared to 5.0%, which suggests that the investment has a positive beta.
- The inferred cost of equity capital seems low compared to 5.0%, which suggests that the investment has a positive beta.
Feedback
Correct
Marks for this submission: 4.00/4.00.
…Please click on the Icon below to purchase the FULL SOLUTION PACKAGE at only $10
Question 4 – Cost of Capital Measures
Question text
Estimating WACC and Expected Growth in Dividends Model
United Parcel Service Inc. was trading at $97.53 at December 31, 2018. Its dividend per share was $3.84, its market beta was estimated to be 1.44, its average pretax borrowing rate was 2.6%, and its assumed statutory tax rate was 22.4%, consisting of the 21% federal rate plus the 1.4% state and local rate, net of any federal benefits. UPS’s market value of equity (market capitalization) was $83.90 billion, computed as 860.2386 million shares times its $97.53 price, and its total market value (enterprise value) was $107.19 billion, computed as $83.90 billion in equity plus the fair value of long-term debt of $23.29 billion (disclosed in note 8 of the financial statements). Assume a risk-free rate of 2.1% and a market risk premium of 5% to answer the following requirements.
(a) Estimate UPS’s cost of debt capital, cost of equity capital, and weighted average cost of capital. (Round your answers to one decimal place.)
Calculate the weighted average cost of capital. (Use your rounded answers from above. Do not round until your final answer. Round to one decimal place.)
(b) Using the dividend discount model, and assuming a constant perpetuity at its dividend level, estimate UPS’s intrinsic value per share. (Use the rounded cost of equity capital calculated in (a). Round your answer to two decimal places.)
(c) Using the Gordon Growth DDM, and assuming next period’s dividends equal $3.84 and grow at a constant rate for each period thereafter, infer the market’s expected growth in dividends that are necessary for UPS’s intrinsic value to equal its observed price per common share. (Do not round until your final answer. Round to one decimal place.)
Discuss the reasonableness of this growth factor.
- The growth in dividend factor is close to what was expected due to the fact DDM places the correct amount of weight on the dividends beyond the forecast horizon.
- The growth in dividend factor is higher than expected due to the fact DDM places a tremendous amount of weight on the dividends beyond the forecast horizon.
- The growth in dividend factor is lower than expected due to the fact DDM places a tiny amount of weight on the dividends beyond the forecast horizon.
Feedback
Correct
Marks for this submission: 6.00/6.00.
…Please click on the Icon below to purchase the FULL SOLUTION PACKAGE at only $10
Question 5 – Cost of Capital Measures
Question text
Estimating Cost of Debt Capital
The December 31, 2018, partial financial statements taken from the annual report for AT&T Inc. follow.
| Consolidated Statements of Income | ||
|---|---|---|
| Dollars in millions except per share amounts | 2018 | 2017 |
| Operating revenues | ||
| Service | $152,345 | $145,597 |
| Equipment | 18,411 | 14,949 |
| Total operating revenues | 170,756 | 160,546 |
| Operating expenses | ||
| Equipment | 19,786 | 18,709 |
| Broadcast, programming and operations | 26,727 | 21,159 |
| Other cost of services (exclusive of depreciation and amortization show separately below) | 32,906 | 37,942 |
| Selling, general and administrative | 36,765 | 35,465 |
| Abandonment of network assets | 46 | 2,914 |
| Depreciation and amortization | 28,430 | 24,387 |
| Total operating expenses | 144,660 | 140,576 |
| Operating income | 26,096 | 19,970 |
| Other income (expense): | ||
| Interest expense | (7,957) | (6,300) |
| Equity in net income of affiliates | (48) | (128) |
| Other income (expense) – net | 6,782 | 1,597 |
| Total other income (expense) | (1,223) | (4,831) |
| Income before income taxes | 24,873 | 15,139 |
| Income tax expense | 4,920 | (14,708) |
| Net income | $19,953 | $ 29,847 |
| Consolidated Balance Sheets — Liabilities and Equity Sections | ||
|---|---|---|
| Dollars in millions except per share amounts, December 31 | 2018 | 2017 |
| Current liabilities | ||
| Debt maturing within one year | $10,255 | $38,374 |
| Accounts payable and accrued liabilities | 43,184 | 34,470 |
| Advanced billed and customer deposits | 5,948 | 4,213 |
| Accrued taxes | 1,179 | 1,262 |
| Dividends payable | 3,854 | 3,070 |
| Total current liabilities | 64,420 | 81,389 |
| Long-term debt | 166,250 | 125,972 |
| Deferred credits and other noncurrent liabilities: | ||
| Deferred income taxes | 57,859 | 43,207 |
| Post employment benefit obligation | 19,218 | 31,775 |
| Other noncurrent liabilities | 30,233 | 19,747 |
| Total deferred credits and other noncurrent liabilities | 107,310 | 94,729 |
| Stockholders’ equity | ||
| Common stock ($1 par value, 14,000,000,000 authorized atDecember 31, 2018 and 2017; issued 7,620,748,598 atDecember 31, 2018 and 6,495,231,088 at December 31, 2017) | 7,621 | 6,495 |
| Additional paid-in capital | 125,525 | 89,563 |
| Retained earnings | 58,753 | 50,500 |
| Treasury stock (339,120,073 at December 31, 2018 and 355,806,544at December 31, 2017, at cost) | (12,059) | (12,714) |
| Accumulated other comprehensive income | 4,249 | 7,017 |
| Noncontrolling interest | 9,795 | 1,146 |
| Total stockholders’ equity | 193,884 | 142,007 |
| Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity | $531,864 | $444,097 |
| Consolidated Statements of Stockholders’ Equity — Excerpts | 2018 | |
|---|---|---|
| Amount in millions except per share amounts, December 31 | Shares | Amounts |
| Common Stock | ||
| Balance at beginning of year | 6,495 | $ 6,495 |
| Issuance of stock | 1,126 | 1,126 |
| Balance at end of year | 7,621 | $7,621 |
| Additional Paid-In-Capital | ||
| Balance at beginning of year | $ 89,563 | |
| Issuance of common stock | 35,473 | |
| Issuance of treasury stock | (115) | |
| Share-based payments | 604 | |
| Balance at end of year | $125,525 | |
| Retained Earnings | ||
| Balance at beginning of year | $50,500 | |
| Net income attributable to AT&T ($2.85 per diluted share) | 19,370 | |
| Dividends to stockholders ($2.01 per share) | (14,117) | |
| Cumulative effect of accounting changes and other adjustments | 3,000 | |
| Balance at end of year | $ 58,753 | |
| Treasury stock | ||
| Balance at beginning of year | (356) | $(12,714) |
| Repurchase of common stock | (20) | (692) |
| Issuance of treasury stock | 37 | 1,347 |
| Balance at end of year | (339) | $(12,059) |
(a) How much interest expense did AT&T incur during 2018?
b) What is the book value of AT&T’s interest-bearing debt at the end of 2018?
(c) Estimate AT&T’s 2018 pretax cost of debt capital. (Round your answer to one decimal place.)
(d) Estimate AT&T’s 2018 effective (that is, average) tax rate from information in its income statement. Round your answer to one decimal place.
(e) Using your rounded answer from (c) above, estimate AT&T’s 2018 after-tax cost of debt capital. The company’s statutory tax rate is: 21%. Round your answer to one decimal place.
Why is it appropriate to use the company’s statutory rate for computing its cost of debt capital? Choose all that apply
- The effective rate should always be used.
- The statutory rate should be used because interest expense is deductible for tax purposes and therefore the after-tax cost of debt should be lower than the pretax cost.
- Using the effective rate in this case would inflate the true cost of borrowing.
- We should actually use an average rate using the statutory rate and the effective rate.
Feedback
Correct
Marks for this submission: 11.00/11.00.
…Please click on the Icon below to purchase the FULL SOLUTION PACKAGE at only $10
Question 6 – Cost of Capital Measures
Question text
Estimating Cost of Equity Capital and Weighted Average Cost of Capital
The December 31, 2018, partial financial statements taken from the annual report for AT&T Inc. (T ) follow.
| Consolidated Statements of Income | ||
|---|---|---|
| Dollars in millions except per share amounts | 2018 | 2017 |
| Operating revenues | ||
| Service | $152,345 | $145,597 |
| Equipment | 18,411 | 14,949 |
| Total operating revenues | 170,756 | 160,546 |
| Operating expenses | ||
| Equipment | 19,786 | 18,709 |
| Broadcast, programming and operations | 26,727 | 21,159 |
| Other cost of services (exclusive of depreciation and amortization show separately below) | 32,906 | 37,942 |
| Selling, general and administrative | 36,765 | 35,465 |
| Abandonment of network assets | 46 | 2,914 |
| Depreciation and amortization | 28,430 | 24,387 |
| Total operating expenses | 144,660 | 140,576 |
| Operating income | 26,096 | 19,970 |
| Other income (expense): | ||
| Interest expense | (7,957) | (6,300) |
| Equity in net income of affiliates | (48) | (128) |
| Other income (expense) – net | 6,782 | 1,597 |
| Total other income (expense) | (1,223) | (4,831) |
| Income before income taxes | 24,873 | 15,139 |
| Income tax expense | 4,920 | (14,708) |
| Net income | $19,953 | $ 29,847 |
| Consolidated Balance Sheets — Liabilities and Equity Sections | ||
|---|---|---|
| Dollars in millions except per share amounts, December 31 | 2018 | 2017 |
| Current liabilities | ||
| Debt maturing within one year | $10,255 | $38,374 |
| Accounts payable and accrued liabilities | 43,184 | 34,470 |
| Advanced billed and customer deposits | 5,948 | 4,213 |
| Accrued taxes | 1,179 | 1,262 |
| Dividends payable | 3,854 | 3,070 |
| Total current liabilities | 64,420 | 81,389 |
| Long-term debt | 166,250 | 125,972 |
| Deferred credits and other noncurrent liabilities: | ||
| Deferred income taxes | 57,859 | 43,207 |
| Post employment benefit obligation | 19,218 | 31,775 |
| Other noncurrent liabilities | 30,233 | 19,747 |
| Total deferred credits and other noncurrent liabilities | 107,310 | 94,729 |
| Stockholders’ equity | ||
| Common stock ($1 par value, 14,000,000,000 authorized at December 31, 2018 and 2017; issued 7,620,748,598 at December 31, 2018 and 6,495,231,088 at December 31, 2017) | 7,621 | 6,495 |
| Additional paid-in capital | 125,525 | 89,563 |
| Retained earnings | 58,753 | 50,500 |
| Treasury stock (339,120,073 at December 31, 2018 and 355,806,544at December 31, 2017, at cost) | (12,059) | (12,714) |
| Accumulated other comprehensive income | 4,249 | 7,017 |
| Noncontrolling interest | 9,795 | 1,146 |
| Total stockholders’ equity | 193,884 | 142,007 |
| Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity | $531,864 | $444,097 |
| Consolidated Statements of Stockholders’ Equity — Excerpts | 2018 | |
|---|---|---|
| Amount in millions except per share amounts, December 31 | Shares | Amounts |
| Common Stock | ||
| Balance at beginning of year | 6,495 | $ 6,495 |
| Issuance of stock | 1,126 | 1,126 |
| Balance at end of year | 7,621 | $7,621 |
| Additional Paid-In-Capital | ||
| Balance at beginning of year | $ 89,563 | |
| Issuance of common stock | 35,473 | |
| Issuance of treasury stock | (115) | |
| Share-based payments | 604 | |
| Balance at end of year | $125,525 | |
| Retained Earnings | ||
| Balance at beginning of year | $50,500 | |
| Net income attributable to AT&T ($2.85 per diluted share) | 19,370 | |
| Dividends to stockholders ($2.01 per share) | (14,117) | |
| Cumulative effect of accounting changes and other adjustments | 3,000 | |
| Balance at end of year | $ 58,753 | |
| Treasury stock | ||
| Balance at beginning of year | (356) | $(12,714) |
| Repurchase of common stock | (20) | (692) |
| Issuance of treasury stock | 37 | 1,347 |
| Balance at end of year | (339) | $(12,059) |
| In mid 2019, Yahoo reports that AT&T has a market beta of: | 0.76 |
| and that its closing stock price at the end of 2018 was: | $28.54 |
| AT&T’s statutory tax rate is: | 21% |
(a) Explain what AT&T’s market beta of 0.76 implies regarding its stock price volatility
It implies that the stock of AT&T is a very stable stock.It implies that the stock of AT&T is a very volatile stock.It implies that the stock of AT&T moves the same as the market index.
(b) Assume that the market risk premium equals 5% and that the risk-free rate equals 2.1%. Estimate AT&T’s cost of equity capital using the CAPM model. Round answer to one decimal place.
(c) Footnote 12 of AT&T’s 10-K reports that the market value of its debt is approximately $180.659 billion. Assume that the company’s after-tax cost of debt is 3.70%. Using this information, estimate AT&T’s weighted average cost of capital.
Round your computation for the intrinsic value of equity to nearest million; then do not round until your final answer. Round final answer to one decimal place.
…Please click on the Icon below to purchase the FULL SOLUTION PACKAGE at only $10




