BUS 5413 Week 3 Research Test 2
Question 1 (1 point)
A measure that does not yield consistent scores and does not measure what it is supposed to measure is ____.
Question 1 options:
both valid and reliable
neither valid nor reliable
valid but not reliable
reliable but not valid
Related: (Solution) BUS 5413 Week 5 Research Test 3
Question 2 (1 point)
One of the measures Rosalyn is including in her study of the effects of environmental enrichment is the score on a standardized scale of intelligence. This is best described as a(n) ____ scale.
Question 2 options:
nominal
ordinal
interval
ratio
Question 3 (1 point)
Checking on whether the new measure is different from measures from which it should, indeed, be different provides an assessment of ____ validity.
Question 3 options:
content
face
discriminant
concurrent
Question 4 (1 point)
When an individual participating in a study tries to guess what the experimenter’s hypothesis is, there is a social threat to construct validity.
Question 4 options:
True
False
Question 5 (1 point)
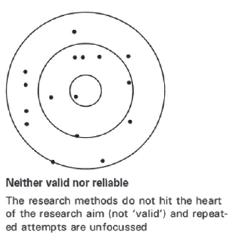
A measure that consistently and accurately measures what is supposed to measure is ____.
Question 5 options:
both valid and reliable
neither valid nor reliable
valid but not reliable
reliable but not valid
Question 6 (1 point)
Leslie is studying test anxiety and administers a test to his research participants that asks them to rate their anxiety in various situations on a scale of 0 (no anxiety) to 10 (the worst anxiety imaginable). He then uses the scores to divide his participants into high, medium, and low anxiety groups. Leslie’s “high-medium-low” scale is best described as an example of a(n) ____ scale.
Question 6 options:
nominal
ordinal
interval
ratio
Question 7 (1 point)
If you could see all random error in a distribution, it would ____.
Question 7 options:
have a variance equal to the mean
sum to zero
shift the mean in a positive direction
be greater than the population variance
Question 8 (1 point)
Cronbach’s Alpha is mathematically equivalent to the average of all possible split-half correlations.
Question 8 options:
True
False
Question 9 (1 point)
Checking a new test to be certain that it contains items that it would be expected to contain based on the relevant literature provides an assessment of ____ validity.
Question 9 options:
content
face
discriminant
concurrent
Question 10 (1 point)
The consistency of the results of two tests constructed in the same way from the same content domain is referred to as ____ reliability.
Question 10 options:
inter-rater
test-retest
parallel-forms
internal consistency
Question 11 (1 point)
The reliability ratio is expressed as ____.
Question 11 options:
var(T) / var(X)
var(X) / var(T)
rel(X) / rel(T)
rel(T) / rel(X)
Question 12 (1 point)
Hannah has developed a scale for assessing social interaction among children with moderate to severe developmental disabilities. Because it is in the early stages, she has many dozens of potential items and decides to create two versions of the test from among her many items and then have individual observers score the same children using the two different versions. Hannah is assessing ____ reliability.
Question 12 options:
| inter-rater |
| test-retest |
| parallel-forms |
| internal consistency |
Question 13 (1 point)
If a test looks as though it measures what it claims to measure is an assessment of ____ validity.
Question 13 options:
convergent
face
discriminant
concurrent
Question 14 (1 point)
In what level of measurement is there a meaningful absolute zero?
Question 14 options:
nominal
ordinal
interval
ratio
Question 15 (1 point)
A measure that yields consistent scores but does not measure what it is supposed to measure is ____.
Question 15 options:
both valid and reliable
neither valid nor reliable
valid but not reliable
reliable but not valid
Question 16 (1 point)
Cronbach’s Alpha is used to overcome limitations associated with reliability assessed using the ____ method.
Question 16 options:
inter-rater
split-half
average inter-item correlation
average item-total correlation
Question 17 (1 point)
The formula X = T + E best describes ____.
Question 17 options:
item response theory
true score theory
the Rasch model
generalizability theory
Question 18 (1 point)
Hannah has developed a scale for assessing social interaction among children with moderate to severe developmental disabilities. Because it is in the early stages, she decides to rate the same children on two different occasions. Hannah is assessing ____ reliability.
Question 18 options:
inter-rater
test-retest
parallel-forms
internal consistency
Question 19 (1 point)
When there is no error in measurement, reliability is ____.
Question 19 options:
0
1
equal to the variability of the distribution
equal to the inverse of the variability of the distribution
Question 20 (1 point)
In ____, research participants do not respond the way they normally would because they are anxious about being tested.
Question 20 options:
hypothesis guessing
evaluation apprehension
researcher expectancies
construct confounding
Question 21 (1 point)
Random error is also called noise.
Question 21 options:
True
False
Question 22 (1 point)
As long as your test is reliable, it need not be valid.
Question 22 options:
True
False
Question 23 (1 point)
The consistency of results across items within a test is referred to as ____ reliability.
Question 23 options:
inter-rater
test-retest
parallel-forms
internal consistency
Question 24 (1 point)
When systematic error affects the mean of a distribution, it is referred to as ____.
Question 24 options:
shifting
variance
bias
regression
Question 25 (1 point)
The proportion of truth in a set of scores across your sample can be thought of as ____.
Question 25 options:
validity
reliability
variability
power
Question 26 (1 point)
Wanda is assessing a new treatment for performance anxiety that involves teaching individuals how to control their breathing. She presents her preliminary results at a student research symposium and is questioned as to whether her intervention affects the cognitive components of performance anxiety. She is being questioned about the possibility of ____.
Question 26 options:
mono-method bias
mono-operation bias
treatment interactions
hypothesis guessing
Question 27 (1 point)
Hannah has developed a scale for assessing social interaction among children with moderate to severe developmental disabilities. Because it is in the early stages, she trains two research assistants in how to use the scale, has them both observe the same children, and compares the scores they give the children. Hannah is assessing ____ reliability.
Question 27 options:
inter-rater
test-retest
parallel-forms
internal consistency
Question 28 (1 point)
Levels of measurement are important because they determine what type of analysis can be used.
Question 28 options:
True
False
Question 29 (1 point)
Random error can drastically affect the average performance for a group.
Question 29 options:
True
False
Question 30 (1 point)
In ____, research participants try to figure out what the experimenter is “really” trying to do.
Question 30 options:
hypothesis guessing
evaluation apprehension
researcher expectancies
construct confounding
Question 31 (1 point)
Jamie has people in her study of taste perception self-identify as “foodies” (people with an intense interest in food who enjoy the adventure of trying new foods) or “non-foodies.” This is best described as an example of a(n) ____ scale.
Question 31 options:
nominal
ordinal
interval
ratio
Question 32 (1 point)
With true score theory, ____ error is considered to contribute to test scores.
Question 32 options:
random
systematic
environmental
consistent
Question 33 (1 point)
Ordinal scales have absolute zeroes.
Question 33 options:
True
False
Question 34 (1 point)
Wanda is assessing a new treatment for performance anxiety and includes a single assessment for performance anxiety. Her study is at risk for ____.
Question 34 options:
mono-method bias
mono-operation bias
treatment interactions
restricted generalizability
Question 35 (1 point)
The consistency of an observation from one time to another is referred to as ____ reliability.
Question 35 options:
inter-rater
test-retest
parallel-forms
internal consistency
Question 36 (1 point)
Hannah has developed a scale for assessing social interaction among children with moderate to severe developmental disabilities. She decides to look at the interrelationships among the items in the test. Hannah is assessing ____ reliability.
Question 36 options:
inter-rater
test-retest
parallel-forms
internal consistency
Question 37 (1 point)
Combining multiple independent measures to get at a more accurate estimate of a variable is referred to as ____.
Question 37 options:
triangulation
covariation
validation
imputation
Question 38 (1 point)
A measure that measures what it is supposed to measure but does not yield consistent scores is ____.
Question 17 options:
both valid and reliable
neither valid nor reliable
valid but not reliable
reliable but not valid
Question 39 (1 point)
Cohen’s kappa is used to overcome limitations associated with reliability assessed using the ____ method.
Question 39 options:
inter-rater
split-half
average inter-item correlation
average item-total correlation
Question 40 (1 point)
The degree to which different observers give consistent estimates of the same phenomenon is referred to as ____ reliability.
Question 40 options:
inter-rater
test-retest
parallel-forms
internal consistency
Question 41 (1 point)
Donna’s study of time management includes having participants record the amount of time spent studying each day. This is best described as a(n) ____ scale.
Question 41 options:
nominal
ordinal
interval
ratio
Related: (Solution) BUS 5413 Analysis Assignment 4
Solution – BUS 5413 Week 3 Research Test 2
| Questions – Week 3 Research Test 2 | Correct Answer and Explanation – Week 3 Research Test 2 |
| Q1: A measure that does not yield consistent scores and does not measure what it is supposed to measure is ____. | Answer: Neither valid nor reliable Explanation: If a measure is inconsistent and does not measure what it should, it lacks both reliability and validity. |
| Q2: Rosalyn’s measure of intelligence is best described as a(n) ____ scale. | Answer: Interval Explanation: Intelligence scores are measured on an interval scale, where the intervals between scores are meaningful, but there is no true zero. |
| Q3: Checking whether the new measure differs from those it should differ from provides an assessment of ____ validity. | Answer: Discriminant Explanation: Discriminant validity ensures that the test is unrelated to measures it should not be related to. |
…Please click on the Icon below to purchase the full answer at only $10




