MOS 3370 Chapter 4 Practice Problems
Question 1 – Feather Friends, Incorporated, distributes a high-quality wooden
Feather Friends, Incorporated, distributes a high-quality wooden birdhouse that sells for $20 per unit. Variable expenses are $10 per unit, and fixed expenses total $190,000 per year. Its operating results for last year were as follows:
| Sales (23,000 units) | $ | 460,000 |
| Variable expenses | 230,000 | |
| Contribution margin | 230,000 | |
| Fixed expenses | 190,000 | |
| Operating income | $ | 40,000 |
Required:
Answer each question independently based on the original data:
1. What is the product’s CM ratio?
2. Use the CM ratio to determine the break-even point in sales dollars.
3. Assume this year’s total sales increase by $40,000. If the fixed expenses do not change, how much will operating income increase?
Assume that the operating results for last year were as in the question data.
4-a. Compute the degree of operating leverage based on last year’s sales.
4-b. The president expects sales to increase by 16% next year. Using the degree of operating leverage from last year, what percentage increase in operating income will the company realize this year? Calculate the dollar increase in operating income.
5. The sales manager is convinced that a 12% reduction in the selling price, combined with a $32,000 increase in advertising, would increase this year’s unit sales by 30%.
a. If the sales manager is right, what would be this year’s operating income if his ideas are implemented?
b. If the sales manager’s ideas are implemented, how much will operating income increase or decrease over last year?
6. The president does not want to change the selling price. Instead, he wants to increase the sales commission by $1 per unit. He thinks that this move, combined with some increase in advertising, would increase this year’s unit sales by 30%. How much could the president increase this year’s advertising expense and still earn the same $40,000 operating income as last year?
Question 2
Minden Company introduced a new product last year for which it is trying to find an optimal selling price. Marketing studies suggest that the company can increase sales by 4,000 units for each $2 reduction in the selling price. The company’s present selling price is $62 per unit, and variable expenses are $28 per unit. Fixed expenses are $620,000 per year. The present annual sales volume (at the $62 selling price) is 16,500 units.
Required:
1. What is the present yearly operating income or loss?
2. What is the present break-even point in unit sales and in dollar sales? (Round intermediate calculations and final answers to the nearest whole number.)
3. Assuming that the marketing studies are correct, what is the maximum annual profit that the company can earn? At how many units and at what selling price per unit would the company generate this profit?
4-a. What would be the break-even point in unit sales and in dollar sales using the selling price you determined in (3) above (e.g., the selling price at the level of maximum profits)? (Round intermediate calculations and final answers to the nearest whole number.)
Question 3 – Smithen Company, a wholesale distributor, has been
Smithen Company, a wholesale distributor, has been operating for only a few months. The company sells three products—sinks, mirrors, and vanities. Budgeted sales by product and in total for the coming month are shown below based on planned unit sales as follows:
| Units | Percentage | ||||
| Sinks | 1,000 | 50 | % | ||
| Mirrors | 500 | 25 | % | ||
| Vanities | 500 | 25 | % | ||
| Total | 2,000 | 100 | % | ||
| Product | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sinks | Mirrors | Vanities | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Percentage of total sales | 48 | % | 20 | % | 32 | % | 100 | % | ||||||||||||||||
| Sales | $ | 480,000 | 100.00 | % | $ | 200,000 | 100.00 | % | $ | 320,000 | 100.00 | % | $ | 1,000,000 | 100.00 | % | ||||||||
| Variable expenses | 60,000 | 12.50 | % | 78,000 | 39.00 | % | 90,000 | 28.13 | % | 228,000 | 22.80 | % | ||||||||||||
| Contribution margin | $ | 420,000 | 87.50 | % | $ | 122,000 | 61.00 | % | $ | 230,000 | 71.88 | % | 772,000 | 77.20 | % | |||||||||
| Contribution margin per unit | $ | 420.00 | $ | 244.00 | $ | 460.00 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Fixed expenses | 740,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating income | $ | 32,000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Break-even point in sales dollars | = | Fixed expenses | = | $740,000 | = | $958,549.22 | |
| Overall CM ratio | 0.77 | ||||||
Break-even point in unit sales:
| Total Fixed expenses | = | $740,000 | = 1,917.10 units | |
| Weighted-average CM per unit | ||||
| $386.00* | ||||
| *($420.00 × 0.50) + ($244.00 × 0.25) + ($460.00 × 0.25) | ||||
As shown by these data, operating income is budgeted at $32,000 for the month, break-even sales dollars at $958,549.22, and break-even unit sales at 1,917.10.
Assume that actual sales for the month total $1,008,000 (2,100 units), with the CM ratio and per unit amounts the same as budgeted. Actual fixed expenses are the same as budgeted, $740,000. Actual sales by product are as follows: sinks, $252,000 (525 units); mirrors, $420,000 (1,050 units); and vanities, $336,000 (525 units).
Required:
1. Prepare a contribution format income statement for the month based on actual sales data. (Round your answers to 2 decimal places.)
2. Compute the break-even point in sales dollars for the month, based on the actual data. (Round your percentage answers to nearest whole percent. Round other intermediate values and final answer to the nearest whole dollar.)
3. Calculate the break-even point in unit sales for the month, based on the actual data. (Do not round your intermediate calculations. Round your final answer to the nearest whole number.)
Question 4 – Active Life manufactures wearable technology
Active Life manufactures wearable technology for a variety of purposes. The Athletics Division produces three models of a watch that monitors heart rate, steps taken, calories burned, distance covered, and other metrics related to personal health. Data for the three models are shown below:
| Basic | Advanced | Elite | |||||||
| Selling price per watch | $ | 160.00 | $ | 240.00 | $ | 360.00 | |||
| Variable expenses per watch: | |||||||||
| Production | 88.00 | 108.00 | 126.00 | ||||||
| Sales commissions | 32.00 | 24.00 | 36.00 | ||||||
| Total variable expenses | 120.00 | 132.00 | 162.00 | ||||||
| Contribution margin per watch: | $ | 40.00 | $ | 108.00 | $ | 198.00 | |||
The Athletics Division has the following fixed costs:
| Per Month | |||
| Fixed production costs | $ | 180,000 | |
| Advertising expense | 150,000 | ||
| Administrative salaries | 78,000 | ||
| Total | $ | 408,000 | |
Sales, in units, over the past two months are shown below. The increased in total watches sold is attributable to a special advertising campaign focused on the Basic model. The manager of the Athletics Division believed there was an opportunity to boost sales for that model during the busy holiday season. The one-time advertising campaign in December cost $10,000.
| Basic | Advanced | Elite | Total | |
| November | 2,000 | 2,000 | 4,000 | 8,000 |
| December | 6,000 | 2,000 | 2,000 | 10,000 |
Required:
1. Without preparing an income statement, calculate operating income in both November and December.
2. This part of the question is not part of your Connect assignment.
3. Compute the Athletics Division’s break-even point in unit sales for November.
4. Has December’s break-even point in units gone up or down from November’s break-even point?
5. Assume the sales mix stays the same in January as it was in December. Calculate the total contribution margin if 12,000 units are sold. Assume no change to the contribution margin per unit for any of the models in January.
Question 5 – Alliance Enterprises is considering extensively modifying
Alliance Enterprises is considering extensively modifying their manufacturing equipment. The modifications will result in less wastage of materials, which will reduce variable manufacturing costs and introduce changes to the production process that will improve product quality. This will allow Alliance to increase the selling price of the product. Annual fixed costs are expected to increase to $690,000 if the modifications are made. Expected fixed and variable costs as well as the selling prices are shown below:
| Cost Item | Existing Equipment | Modified Equipment | ||||
| Selling price per unit | $ | 8 | $ | 10 | ||
| Variable cost per unit | 4 | 4 | ||||
| Fixed costs | 340,000 | 690,000 | ||||
Required:
1. Determine Alliance Enterprises’ break-even point in units with the existing equipment and with the modified equipment.
2. Determine the sales level in units at which the modified equipment will achieve a 20% target profit-to-sales ratio (ignore taxes).
3. Determine the sales level in units at which the modified equipment will achieve $157,500 in after-tax operating income. Assume a tax rate of 30%.
4. Determine the sales level at which profits will be the same for either the existing or modified equipment.
Related: (Solution) MOS 3370 Chapter 5 Practice Problems
Step by Step Answers and Explanation – Chapter 4 Practice Problems
Question 1 Answer
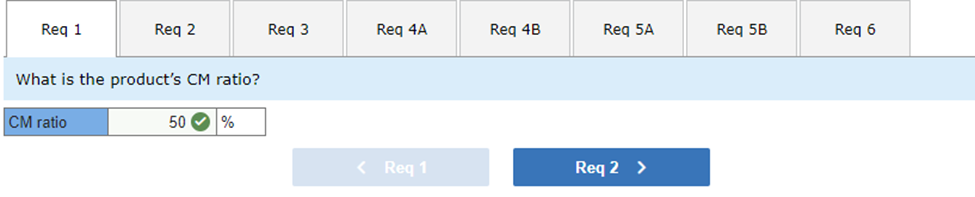
The CM ratio is 50%:
Here is the workings;
| Selling price | $ | 20 | 100 | % | |
| Variable expenses | 10 | 50 | % | ||
| Contribution margin | $ | 10 | 50 | % | |
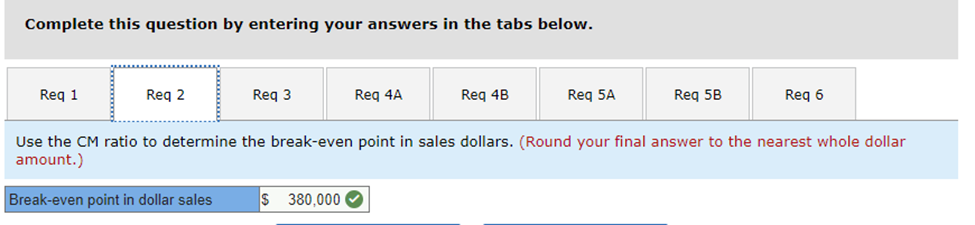
2. Use the CM ratio to determine the break-even point in sales dollars.
| Break-even point in sales dollars | = | Fixed expenses |
| CM ratio |
| Break-even point in sales dollars | = | $190,000 |
| 0.50 |
| Break-even point in sales dollars | = $380,000 |
Please click on the Icon below to purchase the full answer at only $5




