Chapter 2 Practice Problems
Question 1
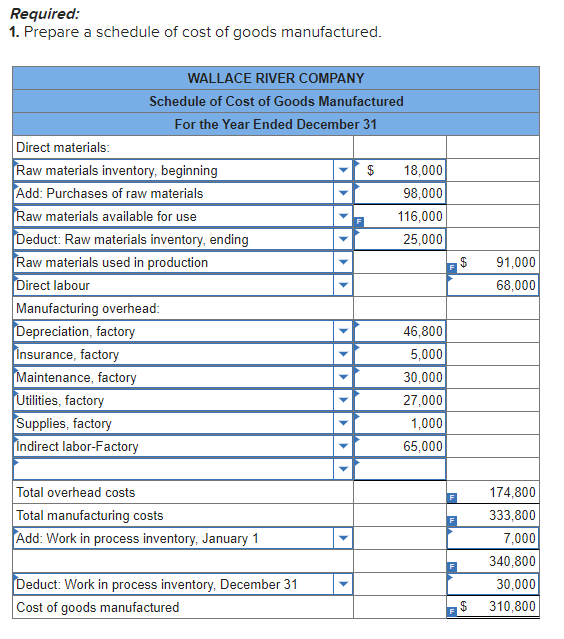
Cost and sales information for the most recent fiscal year are shown below:
| WALLACE RIVER COMPANY | ||
| Cost and Sales Information | ||
| For the Year Ended December 31 | ||
| Purchases of raw materials | $ | 98,000 |
| Raw materials inventory, beginning | 18,000 | |
| Raw materials inventory, ending | 25,000 | |
| Depreciation, factory | 46,800 | |
| Insurance, factory | 5,000 | |
| Direct labour | 68,000 | |
| Maintenance, factory | 30,000 | |
| Administrative expense | 73,200 | |
| Sales | 530,000 | |
| Utilities, factory | 27,000 | |
| Supplies, factory | 1,000 | |
| Selling expense | 83,200 | |
| Advertising expense | 23,200 | |
| Indirect labour, factory | 65,000 | |
| Work in process inventory, beginning | 7,000 | |
| Work in process inventory, ending | 30,000 | |
| Finished goods inventory, beginning | 10,000 | |
| Finished goods inventory, ending | 40,000 | |
Required:
1. Prepare a schedule of cost of goods manufactured.
2. Prepare an income statement.
3. Assume that the company produced 10,000 units of product during the year. What was the average cost per unit for direct materials? What was the average cost per unit for factory depreciation? (Round your answers to 2 decimal places.)
4. Assume that the company expects to produce and sell 15,000 units of product during the coming year. What average cost per unit and what total cost would you expect the company to incur for direct materials and for factory depreciation at this level of activity? Assume that raw materials costs charged by suppliers will not change next year. For factory depreciation, assume that the company uses straight-line depreciation and that the factory equipment has five years of useful life remaining. (Round your answers to 2 decimal places.)
5. This part of the question is not part of your Connect assignment.
Question 2
Carlton Manufacturing Company provided the following details about operations in February:
| Purchases of raw materials | $ | 178,000 |
| Maintenance, factory | 41,800 | |
| Direct labour | 35,700 | |
| Depreciation, factory equipment | 61,400 | |
| Indirect materials, factory | 3,800 | |
| Selling and administrative salaries | 47,300 | |
| Utilities, factory | 29,200 | |
| Sales commissions | 19,100 | |
| Insurance, factory equipment | 4,800 | |
| Depreciation, sales equipment | 23,200 | |
| Advertising expenses | 115,500 | |
| Rent, factory building | ? | |
The company also provided details regarding the balances in the inventory accounts at the beginning and end of the month as follows:
| Beginning of Month | End of Month | |||
| Raw materials | $ | 41,000 | ? | |
| Work in process | 30,400 | ? | ||
| Finished goods | 23,000 | ? | ||
Raw materials used in production cost $192,920, total overhead costs for the month were $219,920, the goods available for sale totalled $424,000, and the cost of goods sold totalled $365,500.
Required:
1-a. Prepare a schedule of cost of goods manufactured of the company’s income statement for the month of February.
1-b. Prepare a schedule cost of goods sold section of the company’s income statement for the month of February.
2. Assume that the dollar amounts given above are for the equivalent of 18,200 units produced during the month. Compute the average cost per unit for direct materials used, and compute the average cost per unit for rent on the factory building. (Round your answers to 2 decimal places.)
3. Assume that in the following month the company expects to produce 23,200 units. What average cost per unit and total cost would you expect to be incurred for direct materials, and for rent on the factory building? Direct materials are a variable cost and rent is a fixed cost. (Round “Unit cost” answers to 2 decimal places.)
4. This part of the question is not part of your Connect assignment.
Question 3
The following information was taken from the accounting records of Mitchell Company for last year:
| Selling expenses | $ | 140,000 |
| Raw materials inventory, January 1 | 90,000 | |
| Raw materials inventory, December 31 | 60,000 | |
| Utilities, factory | 36,000 | |
| Direct labour cost | 150,000 | |
| Depreciation, factory | 162,000 | |
| Purchases of raw materials | 750,000 | |
| Sales | 2,500,000 | |
| Insurance, factory | 40,000 | |
| Supplies, factory | 15,000 | |
| Administrative expenses | 270,000 | |
| Indirect labour | 300,000 | |
| Maintenance, factory | 87,000 | |
| Work in process inventory, January 1 | 180,000 | |
| Work in process inventory, December 31 | 100,000 | |
| Finished goods inventory, January 1 | 260,000 | |
| Finished goods inventory, December 31 | 210,000 | |
Management wants to organize these data into a better format so that financial statements can be prepared for the year.
Required:
1. Prepare a schedule of cost of goods manufactured.
2. Compute the cost of goods sold.
3. Using data as needed from (1) and (2) above, prepare an income statement.
4. Assuming production of finished and semi-finished goods amounted to 412,500 units for the past year, calculate the cost components of the ending finished goods inventory of 55,176 units. (Hint: The categories of costs in the ending inventory are the same as the total manufacturing costs; only the amounts are different.) (Do not round intermediate calculations and round down final answers to nearest whole dollar amount.)
Related: (Solution) Mos3370 Chapter 3 Practice Problems
Step by Step Solution with Explanation – Chapter 2 Practice Problems
Question 1
Here is the complete schedule of Cost of Goods Manufactured
For 100% correct solution with Explanation – Please click on the Icon below to purchase the full answer at only $5




